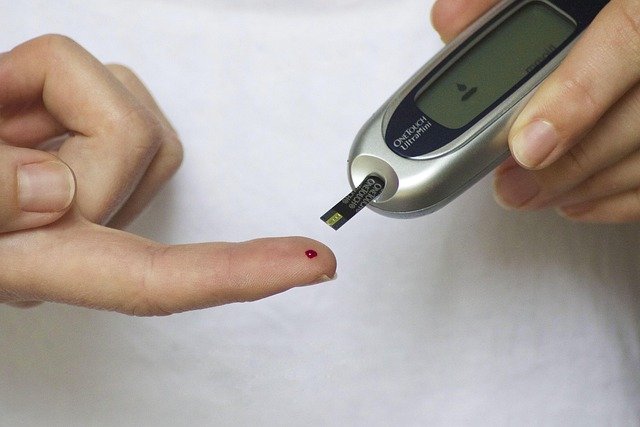
Blood sugar testing is essential for monitoring your health, particularly if you’re at risk for conditions like diabetes. Whether you’re managing a current diagnosis or simply staying proactive with your health, understanding your blood sugar test results can provide valuable insight into your body’s glucose levels and how they relate to your overall well-being.
In this article, we’ll break down what blood sugar tests are, how to interpret the results, and how to manage your levels for optimal health.
What is a Blood Sugar Test?
Blood sugar tests are used to measure the amount of glucose (sugar) in your bloodstream. Glucose is the primary source of energy for your body’s cells, but it’s essential to maintain it at healthy levels. Elevated or low glucose levels can lead to serious health problems, including diabetes and heart disease.
Types of Blood Sugar Tests:
- Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS): Measures your blood sugar levels after fasting for at least 8 hours, typically done in the morning.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Used to diagnose diabetes, this test measures your blood sugar before and after you drink a sugary solution.
- Hemoglobin A1C Test (HbA1c): Shows your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months, offering a longer-term view of your glucose management.
- Random Blood Sugar (RBS): A blood sugar test done at any time of the day, regardless of when you last ate.
Why Do You Need a Blood Sugar Test?
You might need a blood sugar test for various reasons, including:
- Routine checkups to assess your overall health.
- Managing diabetes or prediabetes.
- Symptom evaluation such as unexplained weight loss, excessive thirst, or fatigue.
Interpreting Your Blood Sugar Test Results
Understanding what your test results mean is key to taking charge of your health. Blood sugar levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), and the interpretation varies depending on the type of test.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels:
- Fasting Blood Sugar: 70–99 mg/dL
- Post-Meal (2 hours after eating): Less than 140 mg/dL
- A1C Test: Less than 5.7%
Prediabetes and Diabetes:
- Fasting Blood Sugar:
- 100–125 mg/dL indicates prediabetes (impaired fasting glucose).
- 126 mg/dL or higher suggests diabetes (you need further tests for diagnosis).
- A1C Test:
- 5.7%–6.4% indicates prediabetes.
- 6.5% or higher is consistent with diabetes.
It’s essential to discuss your results with a healthcare provider to get an accurate diagnosis and a plan for treatment.
Understanding A1C Results:
The A1C test is unique because it reflects your blood sugar levels over a few months, rather than just a snapshot of one point in time. Here’s what the A1C ranges mean:
- Normal: Below 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7%–6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher
High Blood Sugar Levels (Hyperglycemia): What They Mean
High blood sugar levels are a sign that your body is not using or producing enough insulin to manage glucose effectively. Hyperglycemia is a serious concern for people with diabetes or those at risk for it.
Symptoms of High Blood Sugar:
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores or infections
Long-Term Risks of High Blood Sugar:
If left unchecked, consistently high blood sugar can lead to complications, including:
- Heart disease and stroke
- Kidney damage
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Vision problems or blindness
Low Blood Sugar Levels (Hypoglycemia): What They Mean
Low blood sugar levels can occur if you skip meals, overexert yourself during exercise, or take too much insulin or medication for diabetes. Hypoglycemia can be dangerous and requires immediate attention.
Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar:
- Shakiness
- Sweating
- Irritability or confusion
- Dizziness
- Hunger
Causes of Low Blood Sugar:
- Skipping meals
- Too much insulin or diabetes medication
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Overexertion during exercise
Immediate Treatment for Low Blood Sugar:
If you experience symptoms of low blood sugar, consume 15-20 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates, such as:
- Glucose tablets
- Fruit juice
- Regular soda (not diet)
Wait 15 minutes and recheck your blood sugar. If it’s still low, repeat the process.
Managing Your Blood Sugar Levels
Whether your blood sugar test results show normal, prediabetic, or diabetic levels, making lifestyle changes can help you manage your health and keep your blood sugar in check.
1. Follow a Healthy Diet
Eating balanced meals with plenty of fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Avoid refined carbs and sugars, which cause blood sugar spikes. A Mediterranean or plant-based diet can be especially beneficial.
2. Stay Active
Exercise helps your body use insulin more efficiently, lowering your blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity, such as walking or cycling, most days of the week.
3. Monitor Your Blood Sugar
Regular blood sugar monitoring allows you to track your progress and make adjustments as needed. If you have diabetes or prediabetes, working with a healthcare professional can help you set personalized goals.
4. Take Medications as Prescribed
If you’re diagnosed with diabetes, your doctor may prescribe medications such as insulin or oral diabetes drugs to help regulate your blood sugar. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions.
When to Consult Your Doctor
If your blood sugar levels are consistently outside the normal range, it’s crucial to consult your doctor. Early detection and intervention can prevent complications and improve your quality of life.
Common Questions About Blood Sugar Test Results
- What is a normal A1C level?
- A normal A1C is below 5.7%. Anything above that may indicate prediabetes or diabetes.
- How often should I get my blood sugar tested?
- For most people, annual testing is recommended. If you have diabetes, your doctor may advise more frequent testing.
- Can blood sugar levels change throughout the day?
- Yes, blood sugar levels naturally fluctuate based on meals, exercise, stress, and other factors.
Taking Charge of Your Health
Understanding your blood sugar test results is the first step in taking control of your health. By knowing your numbers, identifying risks early, and making lifestyle changes, you can keep your blood sugar within a healthy range and reduce the risk of serious complications. Remember, regular testing, a balanced diet, and regular exercise can help you maintain better blood sugar levels and overall well-being.
If you have concerns about your blood sugar levels, consult your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for your health journey.
Learn about blood sugar testing and what your results mean on the official CDC page:
CDC – Blood Sugar Testing